High Manganese Cast Steel Metallographic Analysis Standard
High manganese steel is widely used to cast crusher wear parts, apron feeder pans, shredder wear parts, and mill liners. It is important to get manganese cast steel metallographic analysis standards.
First of all, we need to cut a test part from the cast part.
The microstructure of high-manganese steel after water toughening treatment should be austenite—A (see below) or austenite plus carbide
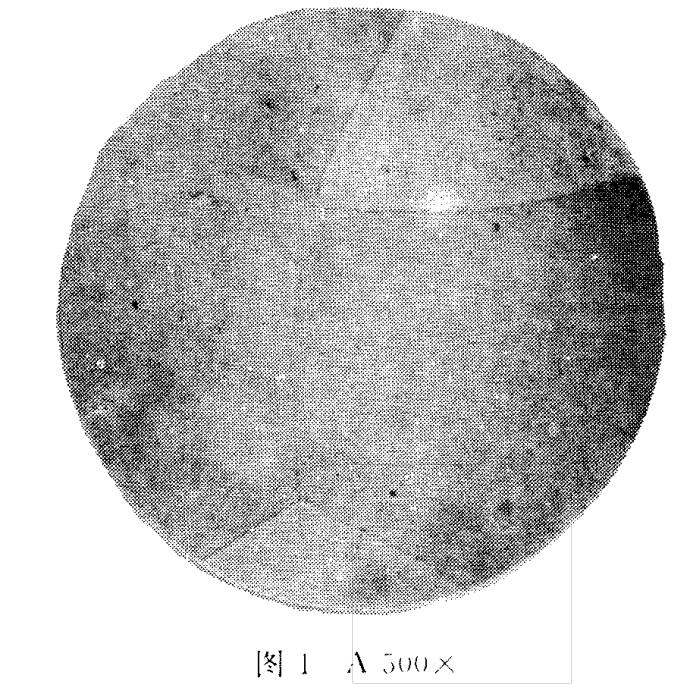
Carbide Rating
- Etching agent: 4% nitric acid alcohol, mixed acid of glycerol (HNO,: HCl: glycerol = 1: 2: 3) and supersaturated picric acid can be selected.
- Magnification: 500X
- Evaluation field of view: 80mm, select the most serious field of view for evaluation.
- Undissolved carbide rating (Please check below table)
Undissolved Carbide Rating Table
| Rate | Characteristic | Part No |
| W1 | The total number of undissolved carbides with an average diameter at the grain boundaries and in the grains smaller than 5 mm is one. | 2 |
| W2 | The total number of undissolved carbides with an average diameter at the grain boundaries and in the grains smaller than 5 mm is two. | 3 |
| W3 | The total number of undissolved carbides with an average diameter at the grain boundaries and in the grains smaller than 5 mm is three. | 4 |
| W4 | The total number of undissolved carbides with an average diameter at the grain boundaries and in the grains smaller than 5 mm more than three. | 5 |
| W5 | Intragrains and grain boundaries have undissolved carbides with an average diameter larger than 5 mm or have aggregates | 6 |
| W6 | Undissolved carbons are massive and distributed along grain boundaries with partial aggregation | 7 |
| W7 | Large amounts of undissolved carbides are distributed along the grain boundaries | 8 |
| Notice: Undissolved carbides with an average diameter of less than 2 mm are not counted in the rating | ||
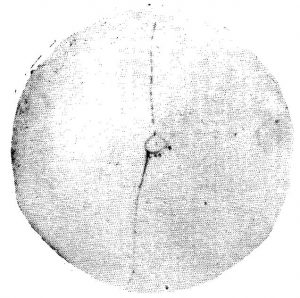
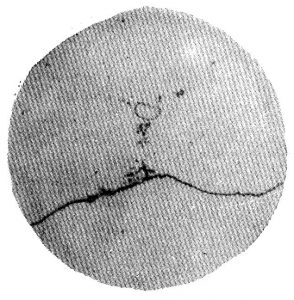
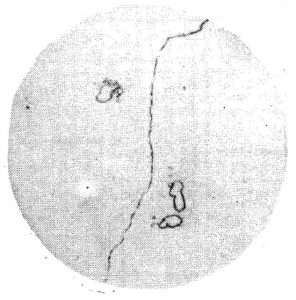
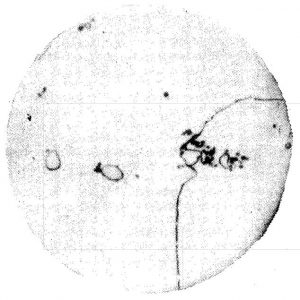
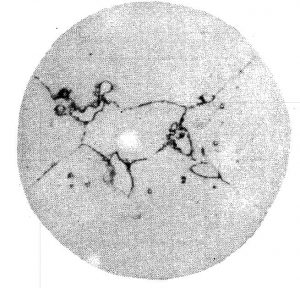
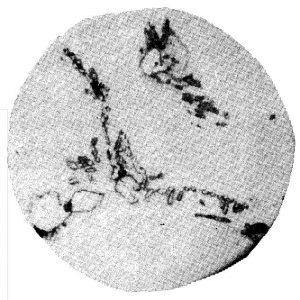
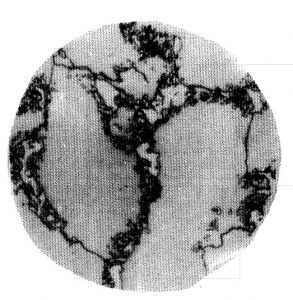
Precipitated Carbide Rating
| Rate | Characteristic | Part No |
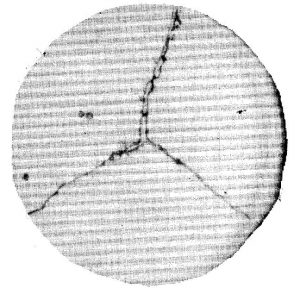
| X1 | A small number of carbides are distributed along the grain boundaries in dots. | 9 |
| X2 | A small number of carbides are distributed along the grain boundaries in dots and short lines. | 10 |
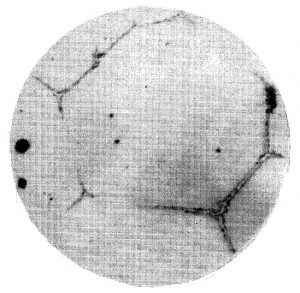
| X3 | The carbides are distributed intermittently along the grain boundaries in thin strips and grains. | 11 |
| X4 | The carbides are distributed in thin lines along the grain boundaries in a network | 12 |
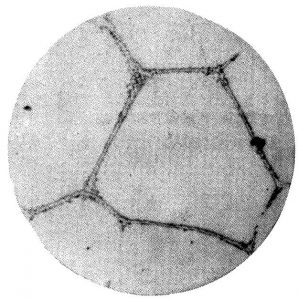
| X5 | The carbides are distributed in a network pattern along the grain boundaries in stripes, and fine needles are precipitated in the crystals. | 13 |
| X6 | The carbides are distributed in strips and feathers in a network pattern along both sides of the grain boundary | 14 |
| X7 | The carbides are distributed in the form of flakes and coarse needles along with the coarse mesh on both sides of the grain boundary. | 15 |
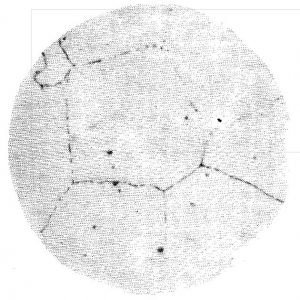 Precipitated Carbide Rating X1
Precipitated Carbide Rating X1
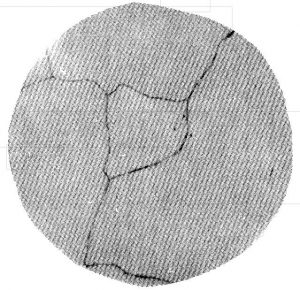
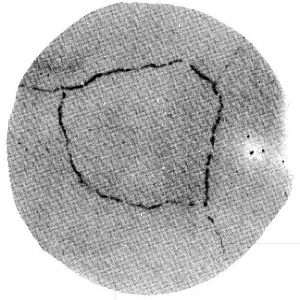 Precipitated Carbide Rating X3
Precipitated Carbide Rating X3
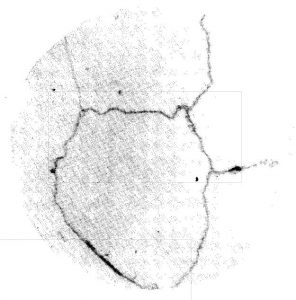
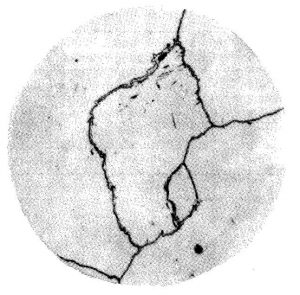
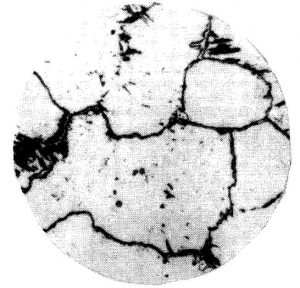
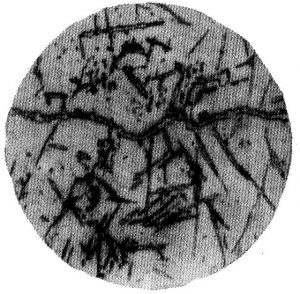
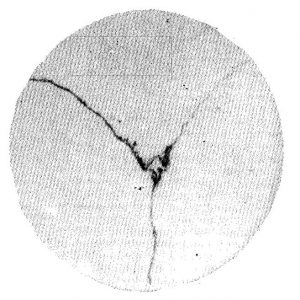
Overheated Carbide Rating
| Rate | Characteristic |
| G1 | Single eutectic carbides distributed along grain boundaries |
| G2 | A small number of eutectic carbides are distributed along grain boundaries or within grains. |
| G3 | Eutectic carbides are intermittently distributed along grain boundaries. |
| G4 | Eutectic carbides are coarsely distributed along grain boundaries |
Post time: Oct-23-2020

